Bank Secrecy Act Phase 1 Exemption
The concept of money laundering is essential to be understood for these working in the monetary sector. It's a process by which dirty cash is transformed into clean money. The sources of the cash in precise are prison and the cash is invested in a manner that makes it look like clear money and hide the identification of the criminal a part of the cash earned.
Whereas executing the monetary transactions and establishing relationship with the brand new prospects or maintaining current customers the obligation of adopting adequate measures lie on every one who is part of the group. The identification of such factor to start with is straightforward to deal with instead realizing and encountering such conditions later on in the transaction stage. The central financial institution in any country gives complete guides to AML and CFT to fight such actions. These polices when adopted and exercised by banks religiously provide enough safety to the banks to discourage such situations.
Under Phase II exemptions transactions in currency by. A Federal State or local government agency or department.

Bsa Aml Ofac Staff Training Ppt Download
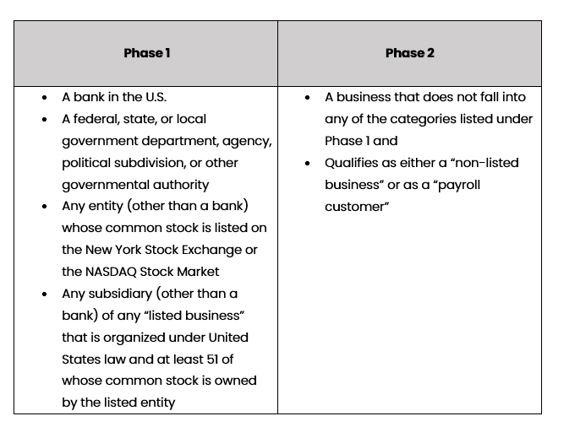
Phase I defines an exempt entity as a bank credit union any government entity and any publicly traded company listed on a major stock exchange.

Bank secrecy act phase 1 exemption. 10 31 CFR 1020315b6 and 31 CFR 1020315b7 specify that exemptions for Phase II customers apply only for transactions through exemptible accounts. Five categories of Phase I exempted entities exist. The exemption provisions were revised and issued in two parts commonly referred to as Phase I and Phase II As of April 30 1996 credit unions were not required to file CTRs on large currency transactions by certain classes of Exempt Persons Exempt Persons are defined in 31 CFR.
The Money Laundering Suppression Act of 1994 MLSA established a two-phase exemption process. No similar statement is found in 31 CFR 1020315b1-5 which applies to Phase. 9 Exemption of a Phase.
A department or agency of the United States of any state or of any political subdivision of any state. Under Phase I exemptions transactions in currency by banks governmental departments or agencies and listed public companies and their subsidiaries may be exempt from reporting. Simplifying the CTR exemption process is consistent with the recommendations in the 2008 report issued by the US.
However the bank could evaluate the customer for potential exemption as a non-listed business customer. The final rule is effective January 5 2009. Under Phase 1 transactions conducted by banks government departments or agencies and listed public companies and their subsidiaries are exempt from CTR reporting.
Phase I Exemptions Phase II Exemptions Certain businesses are ineligible for CTR exemption. Phase I defines an exempt entity as a bank credit union any government entity and any publicly traded company listed on a major stock exchange. 1 A bank 2 A federal state or local government agency or department 3 Any entity exercising governmental authority within the United States 4 any entity whose stock is listed on NYSE ASE or.
Although the annual review for a Phase I exemption government banks listed companies etc is certainly not as extensive as that needed for a Phase II exemption non-listed businesses and payroll customers there is a requirement to verify the status of these exempt persons. Any entity established under federal state or local laws and exercising governmental authority on behalf of the United States or a state or local government. Under Phase 1 transactions conducted by banks government departments or agencies and listed public companies and their subsidiaries are exempt from CTR reporting.
Which is not considered a Phase I exemption. FinCENs regulation identifies five categories of Phase I exempt persons. Here is a table which outlines the Phase 1 and Phase 2 exemptions.
Exemption of a Phase I person covers any transaction in currency with the exempted person not only a transaction in currency conducted through an account. Any entity exercising governmental authority within. The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network FinCEN recently issued a final rule amending the Bank Secrecy Act BSA.
Phase I and Phase II exemptions generally banks governmental entities public companies and domestic companies that have cash intensive businesses or payrolls and a self-executing procedure for banks wishing to take advantage of the exemptions. The bank maintains documentation to support that designated non-listed businesses do not receive more than 50 percent of gross revenue from ineligible business activities. A federal state or local government agency or department.
Certain customers may be exempted from CTR filings. If a Phase I customer no longer is a publicly-traded company the customer is ineligible for a Phase I exemption. Increased Use of Exemption Provisions Could Reduce Currency Transaction Reporting While.
Referred to as Phase I and Phase II exemptions. Franchises or those companies not actually owned by the publicly traded company are not exempt under Phase I. And any federal state or local government entities exercising governmental authority on behalf of the United States or any such state or political subdivision.
The customer is eligible for designation as exempt see categories of Phase I exempt persons and Phase II exempt persons. Government Accountability Office GAO suggesting a variety of ways to improve the CTR exemption process. Under Phase 2 transactions in currency by businesses that meet specific requirements are exempt from CTR reporting.
Phase II defines an exempt entity as a non-listed business or payroll customer as long as. See Bank Secrecy Act. A bank2 to the extent of its domestic operations.
Under Phase 2 transactions in currency by businesses that meet specific requirements are exempt from CTR reporting. BSA and OFAC Compliance - Staff Training. Banks do not need to file a DOEP for any of the 12 Federal Reserve Banks or for any Phase I eligible customer that is a bank to the extent of the banks domestic operations.
A bank to the extent of its domestic operations. The final rule simplifies the regulation allowing credit unions to exempt transactions of certain persons from the requirement to report currency transactions in excess of 10000. Phase I exemptions may be granted for the following exempt persons.
Franchises or those companies not actually owned by the publicly traded company are not exempt under Phase I.

Bank Secrecy Act Bsa Anti Money Laundering

Bank Secrecy Act Bsa Anti Money Laundering

Bsa Who Can Be Ctr Exempt Phase I Vs Phase Ii Pya

Bank Secrecy Act Anti Money Laundering Examination Manual Ffiec
Https Www Stlouisfed Org Federal Banking Regulations Report Ruleid 19253

Bank Secrecy Act Bsa Anti Money Laundering
Bsa Aml Ofac Staff Training Ppt Download
Http Www Dfi Wa Gov Documents Credit Unions Compliance Manual Bsa Overview Pdf
Https Www Acc Com Sites Default Files Resources Vl Public Programmaterial 20070 1 Pdf

Bank Secrecy Act Bsa Anti Money Laundering

Financial Havens Banking Secrecy And Money Laundering Amnet Co Il
Https Www Choosethechief Com Resources 1946f783 0105 4fc4 9198 Cfc8e70b935b Bank 20secrecy 20act Pdf Trackid Bank 20secrecy 20act Pdf
Understanding Ctr Exemptions And Their Practicality

Bank Secrecy Act Many Laws Make Up Bsa Bank Secrecy Act Money Laundering Control Act Currency And Foreign Transactions Reporting Usa Patriot Act Ppt Download
The world of rules can look like a bowl of alphabet soup at times. US cash laundering rules are no exception. We now have compiled an inventory of the top ten cash laundering acronyms and their definitions. TMP Threat is consulting firm focused on protecting financial companies by decreasing danger, fraud and losses. We now have massive bank experience in operational and regulatory danger. Now we have a strong background in program administration, regulatory and operational risk in addition to Lean Six Sigma and Business Course of Outsourcing.
Thus money laundering brings many antagonistic penalties to the organization because of the dangers it presents. It increases the likelihood of major risks and the chance value of the financial institution and finally causes the bank to face losses.
Comments
Post a Comment